On a given microscope, the numerical apertures of the condenser and low power objective lenses are 1.25 and 0.25, respectively. You are supplied with a filter that selects a wavelength of 520 nm. A. What is the limit of resolution on this microscope? B.
SOLVED: Numerical aperture of 0.85. On the same microscope as in question 6, the high-dry objective lens has a limit of resolution of 520 nm. Will you be able to distinguish two
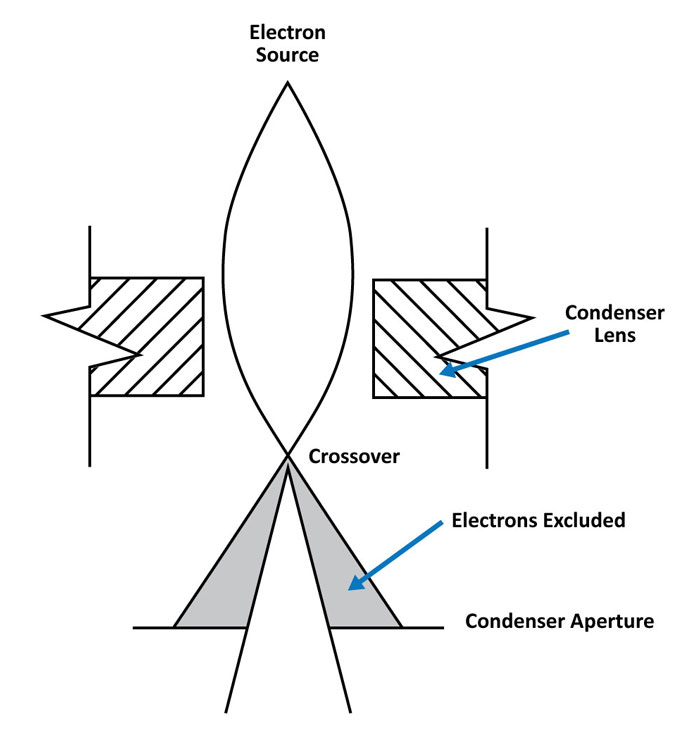
The numerical aperture of a microscope objective is the measure of its Immersion Oil ability to gather light and to resolve fine specimen detail while working at a Resolution fixed object (or specimen) distance. Image-forming light waves pass Practical Hints through the specimen and enter the objective in an inverted cone as illustrated in

Source Image: swift-microscopeworld.com
Download Image
On a given microscope, the numerical apertures of the condenser and low-power objective lenses are 1.25 and 0.25, respectively. You are supplied with a filter that selects a wavelength of 520 nm. A. What is the limit of resolution on this microscope? B.

Source Image: blog.microscopeworld.com
Download Image
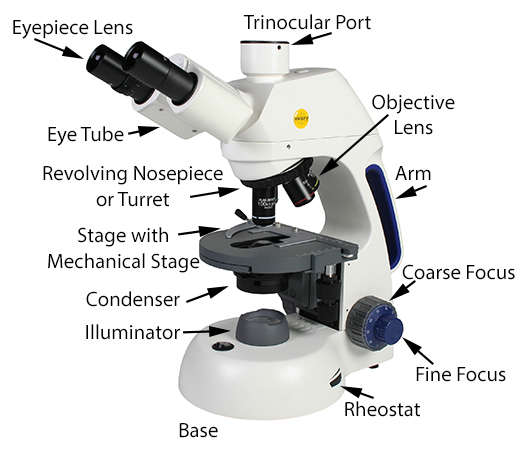
Microscope Parts & Functions – AmScope
The condenser numerical aperture is set to 0.25 and the light cone leaving the condenser is focused on the specimen. In order to operate the tutorial, use the Magnification slider to increase the condenser numerical aperture and observe how opening the iris diaphragm increases the size of the light cone.
Source Image: nanoscience.com
Download Image
On A Given Microscope The Numerical Apertures Of The Condenser
The condenser numerical aperture is set to 0.25 and the light cone leaving the condenser is focused on the specimen. In order to operate the tutorial, use the Magnification slider to increase the condenser numerical aperture and observe how opening the iris diaphragm increases the size of the light cone.
Chapter 7 Lenses. C. Robert Bagnell, Jr., Ph.D., 2012. Lenses are the microscope’s jewels. Understanding their properties is critical in understanding the microscope. Objective, condenser, and eyepiece lenses have information about their properties inscribed on their housings. Table 7.1 is an example from objective lenses.
Scanning Electron Microscopy | Nanoscience Instruments
. On a given microscope, the numerical apertures of the condenser and low power objective lenses are 1.25 and 0.25, respectively. You are supplied with a filter that selects a wavelength of 520nm. a.) What is the limit of resolution on this microscope? Please be specific to how you came up with this answer, what formula did you use? b.)
Microscope World Blog: Microscope Condenser and Aperture Diaphragm

Source Image: blog.microscopeworld.com
Download Image
Condenser controls | Science Toys
. On a given microscope, the numerical apertures of the condenser and low power objective lenses are 1.25 and 0.25, respectively. You are supplied with a filter that selects a wavelength of 520nm. a.) What is the limit of resolution on this microscope? Please be specific to how you came up with this answer, what formula did you use? b.)
Source Image: scitoys.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Numerical aperture of 0.85. On the same microscope as in question 6, the high-dry objective lens has a limit of resolution of 520 nm. Will you be able to distinguish two
On a given microscope, the numerical apertures of the condenser and low power objective lenses are 1.25 and 0.25, respectively. You are supplied with a filter that selects a wavelength of 520 nm. A. What is the limit of resolution on this microscope? B.

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Microscope Parts & Functions – AmScope
On a given microscope, the numerical apertures of the condenser and low-power objective lenses are 1.25 and 0.25, respectively. You are supplied with a filter that selects a wavelength of 520 nm. A. What is the limit of resolution on this microscope? B.

Source Image: amscope.com
Download Image
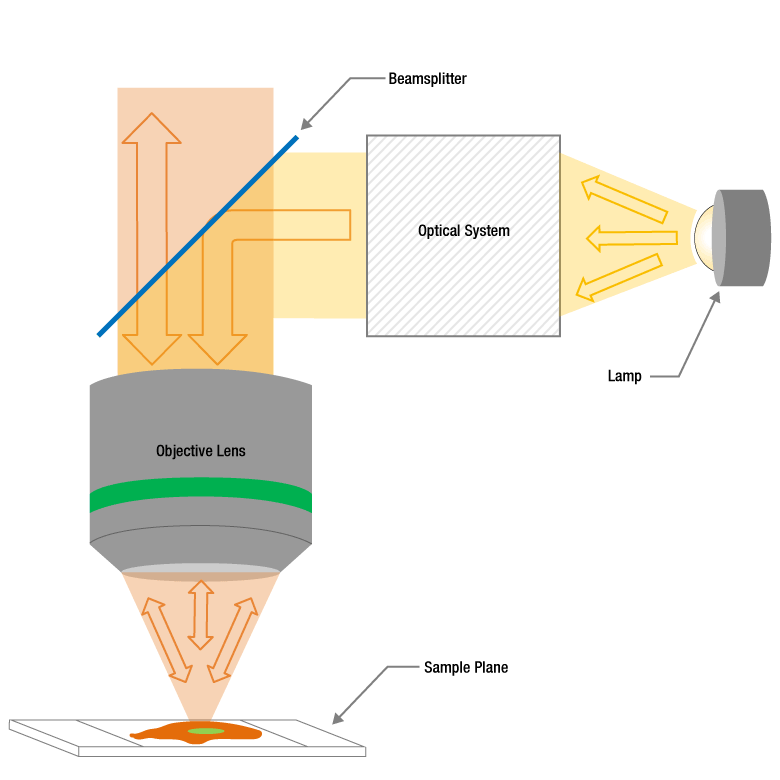
A Microscope’s Condenser Affects Image Resolution
On a given microscope, the numerical apertures of the condenser and low-power objective lens are 1.25 and 0.25, respectively. You are supplied with a filter that selects a wavelength of 520 nm. … Condenser. concentrates the light source and uniformly illuminates the specimen. objective lens. lens that first produces magnification of the specimen.
Source Image: thorlabs.com
Download Image
Microscope World Blog: Microscope Condenser and Aperture Diaphragm
The condenser numerical aperture is set to 0.25 and the light cone leaving the condenser is focused on the specimen. In order to operate the tutorial, use the Magnification slider to increase the condenser numerical aperture and observe how opening the iris diaphragm increases the size of the light cone.

Source Image: blog.microscopeworld.com
Download Image
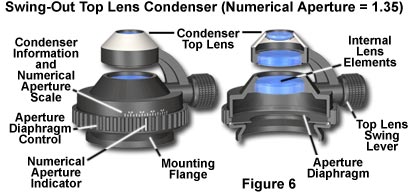
Anatomy of a Microscope – Substage Condensers | Olympus LS
Chapter 7 Lenses. C. Robert Bagnell, Jr., Ph.D., 2012. Lenses are the microscope’s jewels. Understanding their properties is critical in understanding the microscope. Objective, condenser, and eyepiece lenses have information about their properties inscribed on their housings. Table 7.1 is an example from objective lenses.
Source Image: olympus-lifescience.com
Download Image
Condenser controls | Science Toys
Anatomy of a Microscope – Substage Condensers | Olympus LS
The numerical aperture of a microscope objective is the measure of its Immersion Oil ability to gather light and to resolve fine specimen detail while working at a Resolution fixed object (or specimen) distance. Image-forming light waves pass Practical Hints through the specimen and enter the objective in an inverted cone as illustrated in
Microscope Parts & Functions – AmScope Microscope World Blog: Microscope Condenser and Aperture Diaphragm
On a given microscope, the numerical apertures of the condenser and low-power objective lens are 1.25 and 0.25, respectively. You are supplied with a filter that selects a wavelength of 520 nm. … Condenser. concentrates the light source and uniformly illuminates the specimen. objective lens. lens that first produces magnification of the specimen.